Latest Posts
Monday, April 18, 2022
In the previous post we created an EC2 instance in AWS in this post we are going to connect to that instance on a Linux workstation or server with SSH.
Here are the steps to connect to the EC2 instance using SSH on Linux, this will also work on a Mac as well:
1. Navigate to the folder that contains the key pair file that you've downloaded in the previous post, I store it in the folder /aws/EC2/KeyPair/ folder , so I would type cd /aws/EC2/KeyPair then type ls to see the file in the folder
Wednesday, November 17, 2021
In the previous post we created a load balancers with the target groups, rules, and instances to handle HTTPS traffic. In this post we are going to set up our DNS records in Route 53. So go to the Route 53 dashboard, click on your domain
1. Click on "Create record"
Wednesday, November 10, 2021
In the previous post we created four instances with a Launch Template. In this post we are going to add DNS records in Route 53 and configure our Application Load Balancer with our certificates.
Before we start creating stuff let's take a step back and look at how we want to configure the website. Let's say a bank wants to branch out into investing, so it wants to dedicate to instances to it's investing arm. In our architecture we would have two target groups, one target group handling traffic for https://acmebanking.com and the other target group handling traffic for https://investing.acmebanking.com
We are going to register all four instances on the load balancer.
1. So now we ready to create an Application Load Balancer, give it a name and for the listener add an HTTPS listener to the existing one
Wednesday, November 3, 2021
In the previous post we created our certificates in the Certificate Manager, in this post we are going to create four instances using a Launch Template so that we could use it in our load balancer.
1. We are actually going to use "Launch Template" to create our instances, so click on "Launch Templates" under "Instances" in the EC2 Dashboard
Wednesday, October 27, 2021
In this post we are going to set up our website to serve up https traffic so that our traffic can be encrypted. In this post the first part of the series we are going to request a certificate from the Certificate Manager in AWS.
1. The first thing we need to do is create a certificate, In the AWS search field search for Certificate Manager then click on the drop down auto complete choice.
Wednesday, October 20, 2021
In this pose we are going to implement auto scaling on our instances. Auto scaling is a feature on AWS that automatically scaled horizontally either based on metrics or the health of an instance. In this post we are going to setup auto scaling on an Application Load Balancer.
1. The first thing we have to do is setup an Auto Scaling Group under "Auto Scaling" click on "Auto Scaling Groups"
Wednesday, October 6, 2021
In the previous post we went over how to create a Network Load Balancer, in this post we are going to create one of types of load balancer AWS offers. We are going to create a Application Load Balancer, this balancer is designed to work best with the typical line of business web applications. It deals mostly with the requests/response scenarios on the web, therefore it supports the HTTP, and HTTPS protocols exclusively. It can be setup to respond to the routes that configured or the hosts. It all depends on how your web applications serves the client. In a way it's the easiest load balancer type to understand because it deals with headers, URLs, routes, parameters, query strings and etc.
Before we create the load balancer we need to create more than one instances with a web server because we need to test that the load balancer is able to switch.
1. Create four instances with the user data to create Apache Web Servers with these commands in the User Data for instance, if you need the full instruction on how to create instances with User Data you can read this post .
Wednesday, September 29, 2021
In the previous post we went over how to create a Classic Load Balancer, in this post we are going to create one of types of load balancer AWS offers. We are going to create a Network Load Balancer, this balancer is for websites that require high performance and low latency websites, think of streaming data. If your website needs real time streaming data, this is probably the load balancer for you. It supports layer 4 protocols such as UDP, TLS and TCP protocols. If you need a static IP or Elastic IP assigned to your load balancer this is your only choice because the other two load balancer does not give you the option to assign Elastic IPs.
Before we create the load balancer we need to create more than one instances with a web server because we need to test that the load balancer is able to switch.
1. Create two instances with the user data to create Apache Web Servers with these commands in the User Data for instance, if you need the full instruction on how to create instances with User Data you can read this post
Wednesday, September 22, 2021
If your website starts to become popular, especially if it's not static you might noticed that the performance is starting to degrade. The most logical step is to scale your architecture with a load balancer. AWS offers three types of load balancers, there are:
- Application Load Balancer
- Protocols (HTTP, HTTPS)
- Specializes in web applications, deals with traffic at the request level (layer 7)
- Supports query strings, path routing, parameter routing, IP routing
- Supports IP addresses, Lamda Functions (serverless, microservices), and containers
- Network Load Balancer
- Protocols(TCP, TLS, UDP, TCP_UDP) - Layer 4
- When high performance and low latency is required
- TLS offloading
- Elastic IPs can be assigned
- Classic Load Balancer
- Protocols (TCP, SSL, HTTP, HTTPS) - Layer 4, 7
- Old generation, not recommended unless you are running EC2-Classic instance
Wednesday, August 25, 2021
In most scenarios you don't want to expose all of your servers to be public facing. You probably want to configure your network so that only the server that is hosting your web application is public facing. What you want to do is put your web application on the public subnet and your backend servers on the private subnet. This private subnet can access the internet through a NAT gateway for software updates and other functions that require internet access. However, the outside world cannot establish a connection to servers in the private subnet. The NAT gateway resides in the public subnet, acting as a bridge between the public subnet and private subnet.
Wednesday, August 11, 2021
When an instance is created in AWS a public and private IP is assigned to the instance. The private IP does not change, but the public IP address changes each time the instance reboot or is stopped. On reboot you might be lucky enough to grab the same public IP, but it's not guaranteed. But on stoppage you will definitely be assigned a new public IP.
That's probably not a good thing a real world situation, that's where an Elastic IP comes into play. An Elastic IP is a static IP that when assigned does not change. However, there's no free lunch so you will be charged for it. So only create one if you really need it. I would recommend that you use the public DNS instead when you are not in production. Say the development and test environment. You might want to spend some money on the staging environment to mirror production as close as possible.
In the following section I will show you how to create an Elastic IP and assign it to an instance. You probably want to delete it after you create it if you do not want to pay. Only keep it if you want to use it.
Wednesday, July 28, 2021
User Data in an instance allows you run commands while your instance boots up. In the previous posts we just plain vanilla instances so far. But in this post we are going to install the Apache Httpd service when we create our instance using User Data.
Here are the steps to create an instance with User Data:
In this blog we are going to start our journey into AWS infrastructure with the creation of an EC2 instance which is probably the most common task you'll ever do.Wednesday, June 23, 2021
So far we have connected to our EC2 instance with the terminal on Linux and Putty on Windows. There is another option that you can perform and it only requires that you have a browser. You must have an Amazon Linux Version 2 instance for this to work, at least that's what I think.
On the instances page on the AWS console click on the "Connect" button while the instance is selected
Wednesday, June 16, 2021
On the previous post we connect to our EC2 instance using SSH on Linux now I will show you how to connect to the EC2 instance using Putty on Windows
Here are the steps to connect to our EC2 instance on Windows:
1. Download and install Putty from here
2. Open PuttyGen from the start menu, and select your .pem file and convert it to a .pkk file
Once it's open select "File", then "Load private key", then select your .pem file
Wednesday, June 2, 2021
Tuesday, June 1, 2021
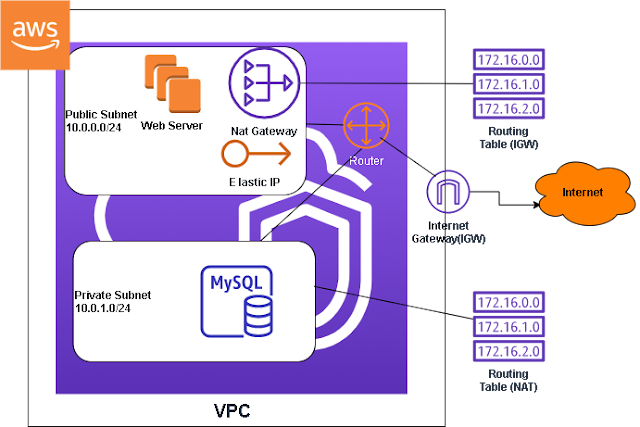
In the next month or so I will start a series of blog posts that will take you from scratch on how to deploy an Angular application that makes API calls from an Asp.Net Core web api backend using Entity Framework Core as it's ORM and MySQL as the database. Most tutorials would end there, but I will take it further and deploy the application on AWS so that it lives on the world wide web. Since I don't want to start from scratch I will be modernizing the ACME bank application that I've started with AngularJS. If you are working with AngularJS you know that it's time to update and upgrade because it's at its' last legs and Angular is the future. Some say the journey is more rewarding than the destination. I hope, you will join me on this journey. Thank you, here is a diagram of what's to come
Friday, December 14, 2018
Tuesday, July 11, 2017
Here are the steps to get the automation scripts for your VM in Azure:
1. Log into the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com
2. Click on "Virtual Machines"
Tuesday, June 6, 2017
Tuesday, May 30, 2017
Follow the steps below to create a new Azure "Cloud Service":
1. Once you are logged into the Azure Portal click on the "Coud Services" on left hand side